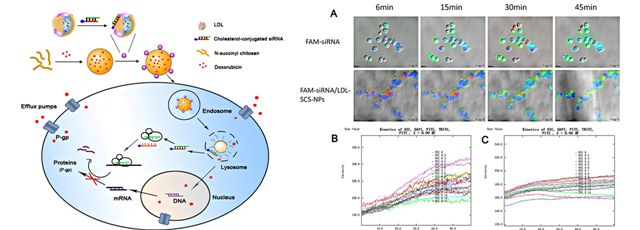
[1] Low-density lipoprotein-coupled N-succinyl chitosan nanoparticles co-delivering siRNA and doxorubicin for hepatocyte-targeted therapy
Qiao-ling Zhu, Yi Zhou, Min Guan, Xiao-feng Zhou, Shu-di Yang, Yang Liu, Wei-liang Chen, Chun-ge Zhang, Zhi-qiang Yuan, Chun Liu,Ai-jun Zhu, Xue-nong Zhang
Biomaterials 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.03.088 (SCI一区,IF=7.604)
Developing safe and effective carriers of small interference RNA (siRNA) is a significant demand for the systemic delivery of siRNA. In this study, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) was isolated from human plasma and loaded with cholesterol-conjugated siRNA to silence the multidrug resistant gene of tumors. Chol-siRNA/LDL coupled N-succinyl chitosan nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin (Dox-siRNA/LDL-SCS-NPs) were then prepared and characterized. In vitro antitumor activity revealed that cell growth was significantly inhibited. The accumulation of Dox by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry showed that LDL-coupled nanoparticles were more easily take up than Dox-SCS-NPs. Results of confocal microscopy and reverse transcription-PCR revealed the highly efficient uptake of siRNA and the decrease in mdr1 mRNA expression. LDL-coupled nanoparticles protected siRNA from macrophage phagocytosis by dynamic observation using live cell station. In vivo tumor targeting suggested that Cy7-labeled Dox-LDL-SCS-NPs were markedly accumulated in an analyzed in situ liver tumor model. Results indicated that LDL-SCS-NPs were effective tumor-targeting vectors and that the preparation form may provide a new strategy for co-delivering siRNA and antitumor drugs.
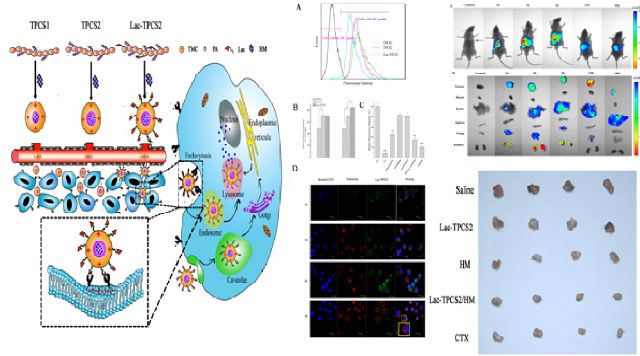
[2]Novel self-assembled micelles based on palmitoyl-trimethylchitosan for efficient delivery of harmine to liver cancer
Yong-Yan Bei, Zhi-Qiang Yuan, Liang Zhang, Xiao-Feng Zhou, Wei-Liang Chen, Peng Xia, Yang Liu, Ben-Gang You, Xiao-Juan Hu, Qiao-Ling Zhu, Chun-Ge Zhang, Xue-Nong Zhang ,Yong Jin
Expert opinion on drug delivery: 2014: 11(6) , 二区,IF 4.869
Backgroud:Polymeric micelles is a safe and effective delivery system, which belong to the targeted delivery system (TDS). An anticancer drug, harmine (HM) is a hydrophobic drug with much adverse effects when used for treatment of liver cancer. Chitosan (CS) is a polysaccharide and can be modified to be an amphiphilic polmer which could self-assemble into micelles and be applied for delivery of hydrophobic drugs.
Objectives:To synthesize three kinds of novel biodegradable polymers, designated as palmitoyl-trimethyl-CS (TPCS)1, TPCS2 and Lac-TPCS2, and investigate their efficiency and mechanism of delivery HM to liver tumors in vitro and in viro.
Results: The self-assembled micelles presented satisfactory particle size (~ 200 nm) and drug release characteristics in vitro. It’s proved that Lac-TPCS2/HM may enter HepG2 cell through endocytosis. Antitumor experimentsin vivo revealed that Lac-TPCS2/HM could significantly inhibit tumor growth and extend the lifetime of mice bearing H22 tumors after intravenous administration. Subsequently in vivo near- infrared fluorescence imaging results demonstrated a satisfactory livertumor-targeting effect of Lac-TPCS2/HM.
Conclusion:Three novel polymers hold great potential in the development of nanomedicine for treatment of liver tumors, in particular Lac-TPCS2 exhibits the greatest antitumor potential through active target effect.
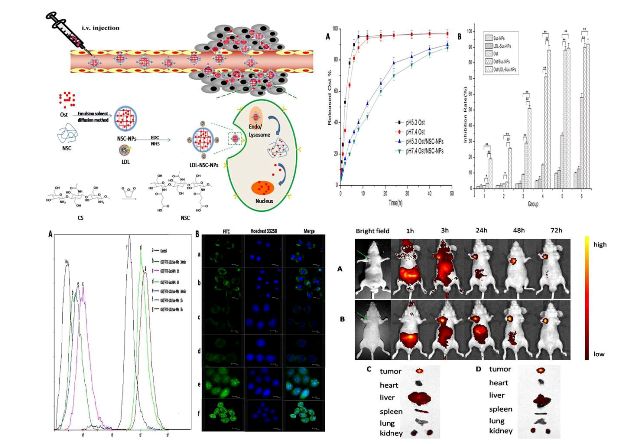
[3]N-Succinyl-chitosan nanoparticles coupled with low-density lipoprotein for targeted osthole-loaded delivery to lipoprotein receptor-rich tumors
Chun-ge Zhang, Qiao-ling Zhu, Yi Zhou, Yang Liu, Wei-liang Chen, Zhi-Qiang Yuan, Shu-di Yang ,Xiao-feng Zhou, Ai-jun Zhu, Xue-nong Zhang, Yong Jin
International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2014:9 二区,IF 3.46
N-Succinyl-chitosan (NSC) was synthesized, and NSC nanoparticles (NPs) -with loaded osthole (Ost/NSC–NPs) were prepared by emulsion solvent diffusion. Subsequently, low density lipoprotein (LDL)-mediated NSC–NPs with loaded osthole (Ost/LDL–NSC–NPs) were obtained by coupling LDL with Ost/NSC–NPs through amide linkage. The average particle size of Ost/NSC–NPs was approximately 145 nm, the entrapment efficiency was 78.28% ± 2.06%, and the drug-loading amount was 18.09% ± 0.17%. The release of Ost from Ost/NSC–NPs in vitro showed a more evident sustained effect than the native material. The half maximal inhibitory concentration of Ost/LDL–NSC–NPs was only 16.23% that of the free Ost at 24 h in HepG2 cells. Ost inhibited HepG2 cell proliferation by arresting cells in the synthesis phase of the cell cycle and by triggering apoptosis. Cellular uptake and subcellular localization in vitro and near-infrared fluorescence real-time imaging in vivo showed that Ost/LDL–NSC–NPs had high targeting efficacy. Therefore, LDL–NSC–NPs are a promising system for targeted Ost delivery to liver tumor.