Prof. Yipeng Wang's group screened nonapeptides with great skin photoprotective effect and revealed underlying mechanisms delaying skin aging
Ultraviolet (UV), the most common environmental stressor to human skin, causes redox imbalance and leads to skin photoaging. Antioxidant peptides (AOPs), bioactive peptides with antioxidant activity, show strong potential in oxidative stress-related diseases due to their great biological activity, strong specificity, and low resistance. Current therapeutic strategies for skin photoaging focus on the rapid scavenging of excess ROS and alleviating UV-induced DNA damage, apoptosis, and inflammatory responses. However, AOPs still suffer from drawbacks such as long amino acid sequences, poor stability, and short half-life. The mechanism of repairing the photoaged skin of AOPs is still unclear.
In recent years, Prof. Yipeng Wang's group from the College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University, has carried out a series of studies on the identification, structural modification, and application of AOPs (Dev Comp Immunol. 2021, 116:103928; Biochimie. 2021, 191:37-50; Future Med Chem. 2019, 11(19):2505-2525; J Med Chem. 2018, 61(15):6846-6857; Protein Pept Lett. 2015, 22(9):776-84). The team recently cooperated with the Dalian University of Technology. On the basis of the above work, natural antioxidant peptides were chosen as templates. After the rational design and structural modification, PWH has been screened as the best candidate from a series of derivatives by measuring antioxidant activity, promoting type I collagen (COL-1), and repairing damaged skin. PWH could alleviate UV-A-induced oxidative stress, restrain pro-inflammatory cytokines production, and protect mitochondrial function, while delaying the photoaging process by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and regulating cellular autophagy in skin cells. Topical applications of PWH were further demonstrated to exhibit significant protection in full-wavelength UV-induced skin aging in mice models both in the prophylaxis and treatment way. In addition, given the good stability and without unwanted toxicity and anaphylaxis, PWH could be a promising candidate for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
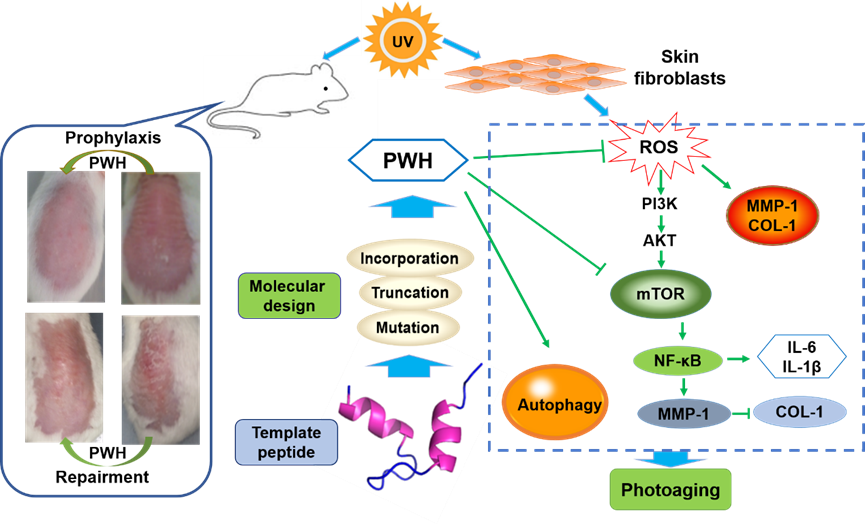
Figure 1. PWH showed great skin photoprotective effect through producing type 1 collagen, blocking PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, and regulating autophagy levels.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070439, 31872223), the Key Research & Development Plan in Social Development of Jiangsu Province (BE2022723), the Suzhou Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project (SNG2022054), the Science and Technology Project of Liaoning Province (2021JH2/10300077), the Priority Academic Program Development of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutes (PAPD).
References:
Wang X, Shi W, Wang K, Ye Z, Wang R, Wang H, Yang H, Xie Z*, Yu H*, Wang Y*.
Rationally Designed Nonapeptides with Great Skin Photoprotective Effect through Producing Type 1 Collagen and Blocking the mTOR Pathway. J Med Chem. 2023 May 29. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00503.
Corresponding author

Prof. Yipeng Wang is a professor and doctoral supervisor of the Department of Biopharmaceuticals, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University. His research field is medicinal protein/peptide discovery, structural modification, and application research. So far, he has published 66 peer-reviewed SCI research papers, which have been cited more than 2000 times (Google scholar). Besides, he has been authorized 58 Chinese patents.
First authors

Xu Wang is a PhD student of the College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University, majoring in medicinal peptide discovery and mechanism research. He graduated from Chongqing University with a Master's degree in Pharmaceutical Chemistry. He has published 14 SCI research papers, including one in J Med Chem during his doctoral study.