Professor Qing-Ri Cao's laboratory publishes a research paper on novel long-acting microsphere technology in Chemical Engineering Journal
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common persistent arrhythmia in adults, which significantly increases the risk of stroke and has become a major global public health challenge. Statistics show that the probability of stroke in AF patients is five times that of the general population. However, traditional oral anticoagulants have obvious drawbacks, such as poor patient compliance, dosage errors, and potential thromboembolic events due to missed doses. Although Apixaban is a direct factor Xa inhibitor with proven efficacy, its requirement for multiple daily doses limits long-term treatment effectiveness. Developing a long-acting and safe delivery system has become a key issue in anticoagulant therapy. Recently, Professor Qing-Ri Cao's team from the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University, in collaboration with the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University and the Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials, Soochow University, published a research paper in Chemical Engineering Journal.
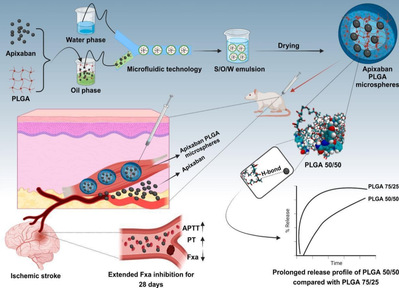
The innovation of this research is threefold: (1) Technological breakthrough—by reprogramming material-drug interactions, it overcomes PLGA 50/50’s poor sustained-release capability, offering new strategies for long-acting formulations. (2) Clinical translation potential—the microsphere preparation could reduce dosing frequency from twice daily to a single injection lasting weeks, significantly improving AF patient compliance and reducing stroke risk. (3) Interdisciplinary integration—combining molecular simulation, microfluidic technology, and pharmacological validation establishes a standardized research paradigm for complex drug delivery system design. This work provides a promising solution for long-term AF-related stroke prevention. If translated clinically, it could reshape current anticoagulation therapy paradigms.
Xue-Ai Liu, a master’s student at the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University, is the first author, and Professor Qing-Ri Cao is the corresponding author.
Xue-Ai Liu, Yaseen Hussain, Jiawen Wang, Ping Xia, Xiang-Xiang Huang, Ming-Wei Huo, Ling-Zhi Shia, Jing-Hao Cui, Beom-Jin Lee, Renyu Huang, Yujin Ji, Minggang Wei, Qing-Ri Cao.Engineering Long-Acting apixaban loaded PLGA microspheres for the treatment of stroke caused by atrial fibrillation. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2025, DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2025.164321
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.164321