Han group reports a new targeted protein degradation tool in Nature Communications
Targeted protein degradation technology uses intracellular degradation machineries to selectively degrade target proteins, showing great potential in drug discovery. These machineries mainly include the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, the autophagy pathway, and the endosome lysosome pathway. Recently, lysosome-targeted chimeras have been reported and have expanded the degradation targets to membrane proteins and extracellular proteins, which is an important breakthrough in the field of targeted protein degradation. However, lysosome-targeted chimeras still face challenges in receptor dependence, synthesis complexity, and the Hook effect, and require further upgradation.
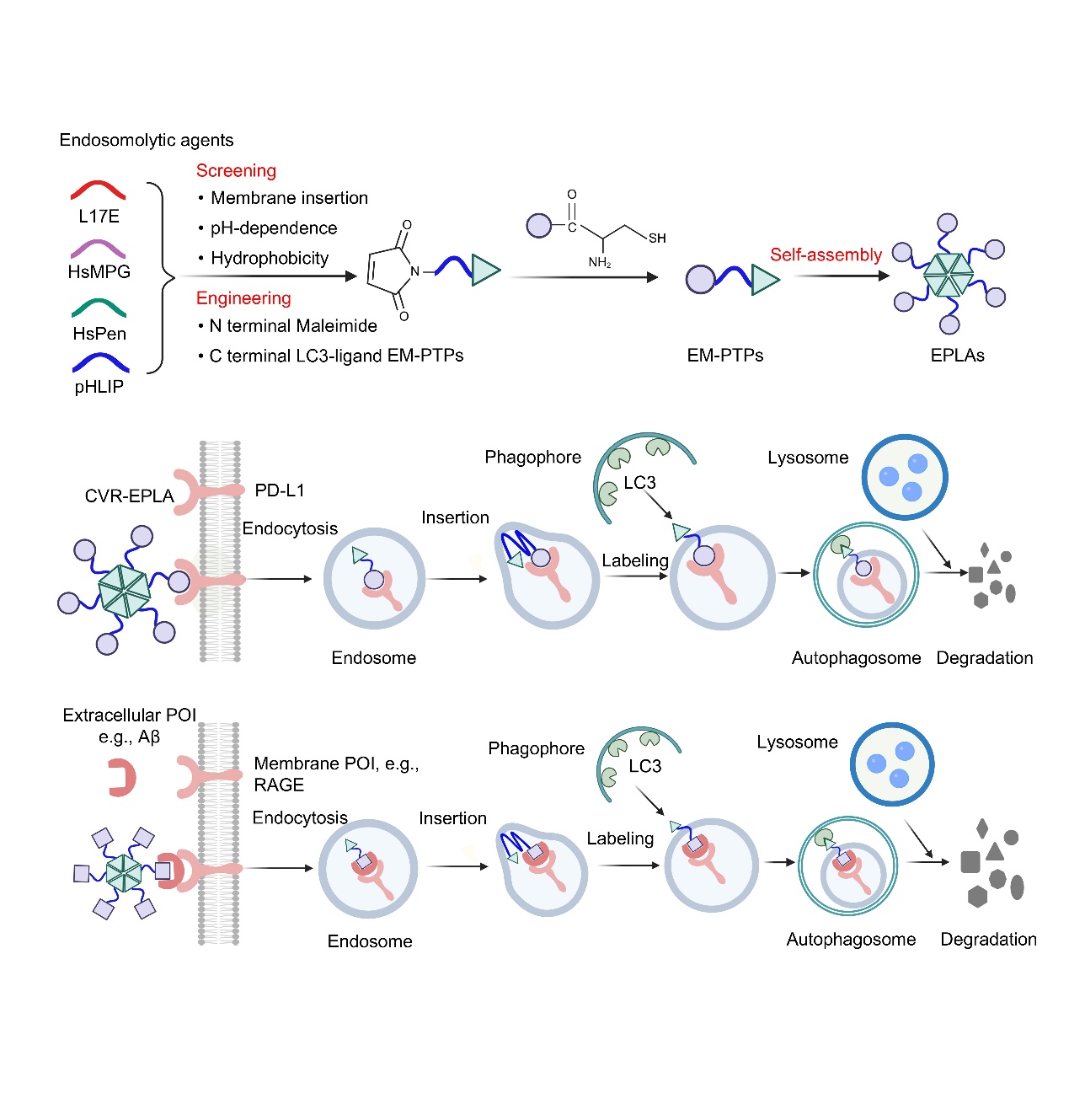
In response to these challenges, Han group at Soochow University innovatively designed a universal degradation tool called EPLA (endosome-phagophore linking assembly). This technology platform integrates endosomes and the autophagy pathway, anchoring phagophore-targeted markers to endosome membrane to induce the spatial proximity between endosomes and phagophores after internalization of target proteins, thereby achieving efficient degradation through the autophagy pathway. EPLA has demonstrated significant modularity and versatility in experiments, successfully degrading various cell membrane proteins (such as PD-L1, RAGE, GRP94) and extracellular pathological proteins (such as amyloid beta and tau protein). In the mouse breast cancer model, PD-L1 was effectively degraded, significantly inhibiting tumor growth, and verifying its potential in therapeutic applications.
This study provides a flexible and efficient platform for autophagic degradation of cell membrane proteins and extracellular proteins, which not only expands the target range of targeted protein degradation technology, but also provides new tools and ideas for basic research and clinical treatments of related diseases. This technology platform is expected to promote further applications of targeted protein degradation in fields such as tumors and neurodegenerative diseases. The relevant results were published in Nature Communications.
Han group is focusing on the overcoming of blood-brain barrier and the design and construction of targeted drug delivery systems, and has made a series of research progresses in the field of brain targeted drug delivery, providing innovative technological paths for precise drug delivery to brain diseases (J Control Release 2019, 303, 117; J Control Release 2021, 329, 934; J Control Release 2024, 369, 458; J Control Release 2024, 375, 116; J Control Release 2025, 378, 763; Acta Pharm Sin B 2021, 11, 1341; Acta Pharm Sin B 2021, 11, 2306; Acta Pharm Sin B 2024, 14, 2716; Adv Funct Mater 2019, 29, 1900259; Adv Sci 2022, 9, 2105854; Adv Healthcare Mater 2021, 10, 2001997; Small 2023, 19, 2300403; Mol Pharm 2021, 18, 2694).
Based on the above progresses, the group innovatively proposed a new degradation platform based on the "endosome autophagosome lysosome" pathway, developing universal degradation tools such as EPLA. It is not only a "transport truck" (delivery), but also a "special scissors" (degradation), achieving the integrated function of "delivery and removal". This platform greatly expands the application boundaries of targeted protein degradation technology, opening up promising new directions for the treatments of various diseases such as brain tumors and neurodegenerative diseases.
This study was jointly conducted by Wang Pan (2021 master), Sun Hang (2022 master), and An Pei (2023 PhD candidate). Professor Han Liang is the corresponding author. This work has received funding from National Innovation of Science and Technology-2030 (Program of Brain Science and Brain-Inspired Intelligence Technology) grant (2021ZD0204000), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20240149), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82574349 and 32171381), Suzhou International Joint Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Brain Diseases, and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Wang, P., Sun, H., An, P. et al. Endosome-phagophore linking assemblies for the degradation of membrane/extracellular proteins. Nat Commun (2025). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-67805-2.