Prof. Dawei Ding's team recently published a paper regarding synergistic tumor treatment in Chemical Engineering Journal
Phototherapy via photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT) has attracted abundant and increasing attention in malignant tumor treatment. Meanwhile, combining chemotherapy and phototherapy via nanoscale drug delivery systems has been widely explored to further improve the therapeutic efficacy of cancers. Nevertheless, deficient reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels caused by the excessive antioxidants (e.g., glutathione (GSH)) in tumor cells and thermoresistance mediated by heat shock proteins (HSPs) represent two pivotal obstacles for phototherapy. In addition, limited control of drug release via conventional nanocarriers results in unpredictable side effects of chemotherapeutic drugs.
To tackle the above-mentioned problems, Prof. Ding's team collaborated with Prof. Yiqiao Hu's team in Nanjing University to develop phase change materials (PCM)-based nanocarriers (a mixture of fatty acid and fatty alcohol) co-delivering the chemotherapeutic drug paclitaxel (PTX), the photosensitizer (PS) IR780 and gambogic acid (GA) to achieve chemotherapy synergized by dually-enhanced phototherapy of breast cancers. Upon the cellular uptake, GA depleted intracellular GSH and blocked the overexpression of HSP90, which in turn simultaneously increased the ROS level and suppressed thermoresistance to enhance the efficacies of PDT and PTT, respectively. Finally, the dually-energized phototherapy and PTT-activated low-dose PTX-based chemotherapy achieved outstanding antitumor performances in vitro and in vivo. In addition, PCM endowed the NPs with the hyperthermia-triggered release of PTX for chemotherapy, which was beneficial in dampening the side effects. In short, the NIR-activatable PCM-based NPs in this study establish a novel strategy of harnessing a single enhancer to boost the efficacies of dual-modal phototherapy and low-dose chemotherapy for improved cancer treatment and reduced side effects. The relevant work was recently published in the top journal of a related field, Chemical Engineering Journal (Impact factor: 16.7), as a paper entitled Dually enhanced phototherapy by gambogic acid and hyperthermia-activated chemotherapy for synergistic breast cancer treatment.
This study was financially supported by the open fund of the State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University, China (Grant no. KF-GN-202102), Priority Academic Program Development of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutes (PAPD), and the Science and Technology Program of Suzhou, China (Grant no. SKJY2021048). Yuhan Wang from Soochow University and Chunyan Yue from Nanjing University were co-first authors of this paper, while Prof. Ding and Prof. Hu were co-corresponding authors.
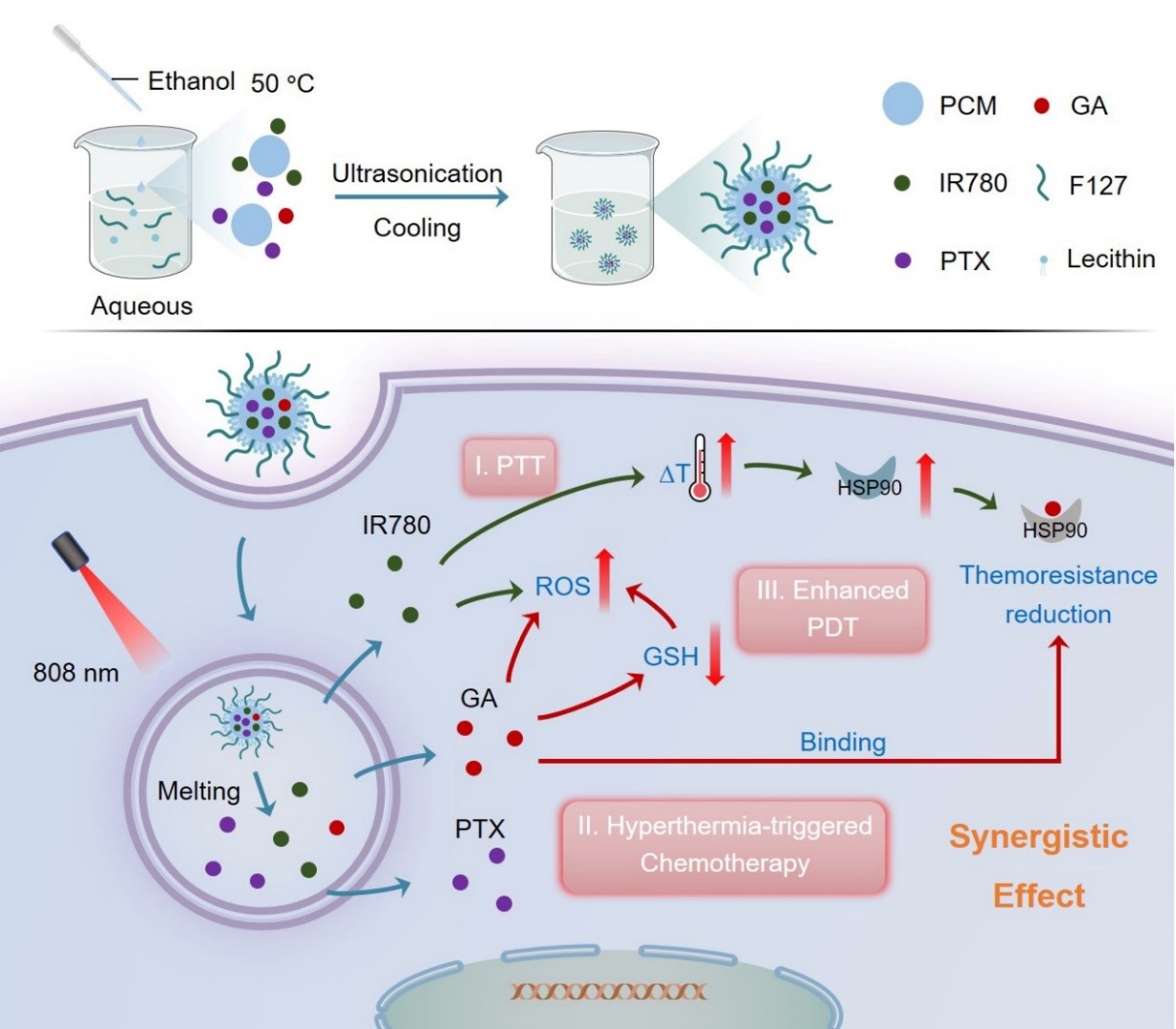
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the preparation of PTX-IR780-GA NPs and their applications in dully enhanced phototherapy and synergistic chemotherapy of breast cancers.
Reference:
Yuhan Wang, Chunyan Yue, Mengyao Zhang, Dazhao Li, Tao Xu, Mengying He, Mengyuan Wang, Yanan Zhao, Zihui Ni, Feng Zhi, Yiqiao Hu*, Dawei Ding*, Dually enhanced phototherapy by gambogic acid and hyperthemia-activated chemotherapy for synergistic breast cancer treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 452, 139108. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894722045879#f0040.
Author information
1. The corresponding author:

Dr. Dawei Ding is a Professor in the College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University as the supervisor of PhD and master's degree students. His team focuses on the application of biocompatible materials, including proteins and fatty acids, in drug delivery systems for the co-delivery of multiple drugs aiming for synergistic tumor treatment. Particularly, chemotherapy and phototherapy are utilized to provoke the host immune responses against tumors via immunogenic cell death (ICD), while the immune checkpoint inhibitors and immunoadjuvants enhance the efficacy of immunity aroused by ICD. In addition, they also devote themselves to the study of microneedles and microfluidics for the development of carrier-free nanodrugs, nanoemulsions, and microparticles in drug delivery applications. Ding's team has published around 20 papers in the related fields, some of which were presented in top journals such as Advanced Materials, ACS Nano, Chemical Engineering Journal, and Advanced Healthcare Materials with first/co-first and corresponding authors. Dr. Ding has also written a chapter in a book published by Elsevier. Moreover, he has also named several patents approved in China, the USA, Japan, and Europe and achieved a few prizes, such as the China Patent Excellence Award (2020) and the Prize of Taizhou Science and Technology Progress (First class, 2015). He is also the invited reviewer of several distinguished journals, including Advanced Functional Materials, Biosensors, Polymers, and Pharmaceutics.
2. The first author

Ms. Yuhan Wang is a Master student from the College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow (Class 2019). Her research interest focuses on synergistic tumor treatment. She has published two papers in the top journal, including Chemical Engineering Journal and Advanced Healthcare Materials, with two more submitted or to be submitted. She is now working at Sanofi China as a clinical research assistant after her graduation in 2022.