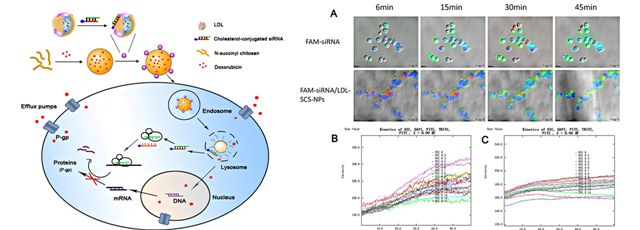
[1] Low-density lipoprotein-coupled N-succinyl chitosan nanoparticles co-delivering siRNA and doxorubicin for hepatocyte-targeted therapy
Qiao-ling Zhu, Yi Zhou, Min Guan, Xiao-feng Zhou, Shu-di Yang, Yang Liu, Wei-liang Chen, Chun-ge Zhang, Zhi-qiang Yuan, Chun Liu,Ai-jun Zhu, Xue-nong Zhang
Biomaterials 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.03.088 (SCI一区,IF=7.604)
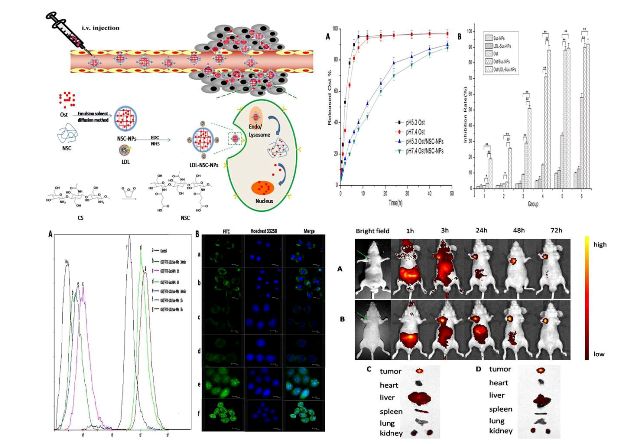
Developing safe and effective carriers of small interference RNA (siRNA) is a significant demand for the systemic delivery of siRNA. In this study, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) was isolated from human plasma and loaded with cholesterol-conjugated siRNA to silence the multidrug resistant gene of tumors. Chol-siRNA/LDL coupled N-succinyl chitosan nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin (Dox-siRNA/LDL-SCS-NPs) were then prepared and characterized. In vitro antitumor activity revealed that cell growth was significantly inhibited. The accumulation of Dox by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry showed that LDL-coupled nanoparticles were more easily take up than Dox-SCS-NPs. Results of confocal microscopy and reverse transcription-PCR revealed the highly efficient uptake of siRNA and the decrease in mdr1 mRNA expression. LDL-coupled nanoparticles protected siRNA from macrophage phagocytosis by dynamic observation using live cell station. In vivo tumor targeting suggested that Cy7-labeled Dox-LDL-SCS-NPs were markedly accumulated in an analyzed in situ liver tumor model. Results indicated that LDL-SCS-NPs were effective tumor-targeting vectors and that the preparation form may provide a new strategy for co-delivering siRNA and antitumor drugs.
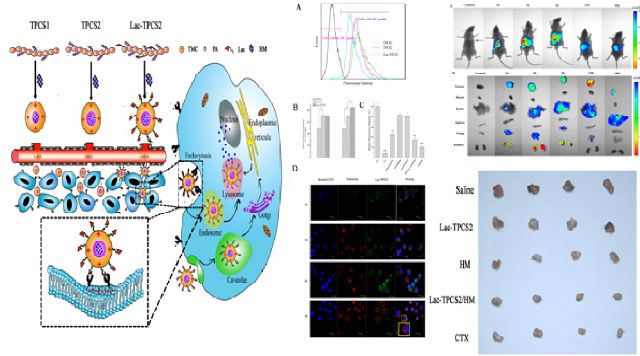
[2]Novel self-assembled micelles based on palmitoyl-trimethylchitosan for efficient delivery of harmine to liver cancer
Yong-Yan Bei, Zhi-Qiang Yuan, Liang Zhang, Xiao-Feng Zhou, Wei-Liang Chen, Peng Xia, Yang Liu, Ben-Gang You, Xiao-Juan Hu, Qiao-Ling Zhu, Chun-Ge Zhang, Xue-Nong Zhang ,Yong Jin
Expert opinion on drug delivery: 2014: 11(6) , 二区,IF 4.869
Backgroud:Polymeric micelles is a safe and effective delivery system, which belong to the targeted delivery system (TDS). An anticancer drug, harmine (HM) is a hydrophobic drug with much adverse effects when used for treatment of liver cancer. Chitosan (CS) is a polysaccharide and can be modified to be an amphiphilic polmer which could self-assemble into micelles and be applied for delivery of hydrophobic drugs.
Objectives:To synthesize three kinds of novel biodegradable polymers, designated as palmitoyl-trimethyl-CS (TPCS)1, TPCS2 and Lac-TPCS2, and investigate their efficiency and mechanism of delivery HM to liver tumors in vitro and in viro.
Results: The self-assembled micelles presented satisfactory particle size (~ 200 nm) and drug release characteristics in vitro. It’s proved that Lac-TPCS2/HM may enter HepG2 cell through endocytosis. Antitumor experimentsin vivo revealed that Lac-TPCS2/HM could significantly inhibit tumor growth and extend the lifetime of mice bearing H22 tumors after intravenous administration. Subsequently in vivo near- infrared fluorescence imaging results demonstrated a satisfactory livertumor-targeting effect of Lac-TPCS2/HM.
Conclusion:Three novel polymers hold great potential in the development of nanomedicine for treatment of liver tumors, in particular Lac-TPCS2 exhibits the greatest antitumor potential through active target effect.
[3]N-Succinyl-chitosan nanoparticles coupled with low-density lipoprotein for targeted osthole-loaded delivery to lipoprotein receptor-rich tumors
Chun-ge Zhang, Qiao-ling Zhu, Yi Zhou, Yang Liu, Wei-liang Chen, Zhi-Qiang Yuan, Shu-di Yang ,Xiao-feng Zhou, Ai-jun Zhu, Xue-nong Zhang, Yong Jin
International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2014:9 二区,IF 3.46